Abstract
Background: Our primary objective is to develop methods that enable early diagnosis of AL or risk of AL during the prodromal decade prior to symptomatic presentation (Weiss et al. J Clin Oncol 2014;32:2699). There are parameters that increase risk of AL such as the presence of a monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) or smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) or having AL-related IGVL genes encoding light-chain production in clonal plasma cells (Zhou et al. J Clin Oncol 2019;37:8010; Kourelis et al. Blood 2017;129:299; Kyle et al. N Engl J Med 2007;356:2582).
Previous studies have shown that clusterin (apolipoprotein J) may play a variety of roles in protein folding disorders, possibly binding and clearing misfolded proteins. Like apolipoprotein E (apoE), clusterin is found in amyloid deposits of all types including the arterial deposits of cerebral amyloid angiopathy; moreover, it interacts cooperatively with apoE in Alzheimer's (Endo et al. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2019;7:12; DeMattos et al. Neuron 2004;41:193). Furthermore, serum levels of clusterin are reduced in patients with AL cardiac involvement (Filippini et al. Glia2021;69:681; Greene et al. Biochemistry 2015;54:268; Greene et al. Am J Pathol2011;178:61; Lee et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun2009;388:256). A previous study has also shown that von Willebrand factor (vWF) levels are significantly elevated in AL patients, possibly due to endothelial cell dysfunction (Kastritis et al. Blood 2016;128:405); AL amyloidosis commonly involves the vasculature.
Seeking additional parameters for likelihood of AL we asked whether the ratio of clusterin to vWF (C/v) in marrow plasma differed among AL, MGUS and SMM patients.
Materials & Methods: λ-isotype MGUS or SMM patients from multiple sites in the USA with a difference between involved and uninvolved FLC > 23mg/L and a κ-to-λ ratio below normal and no evidence of amyloid on prior studies consented to participate in a clinical study screening for AL (NCT04615572) and had bone marrow aspirates sent overnite to Tufts. In addition, newly diagnosed AL patients consented to have blood and marrow aspirates obtained for research on an IRB-approved study. All samples were heparinized and had plasma separated initially and aliquoted for storage at -20o C. We also obtained peripheral blood plasma from normal individuals, ages unknown (Precision for Medicine; Norton, MA). Clusterin and vWF ELISA were performed on thawed plasma following manufacturers’ instructions (R&D Systems; Minneapolis, MN). GraphPad PRISM V5 was used for statistical analyses.
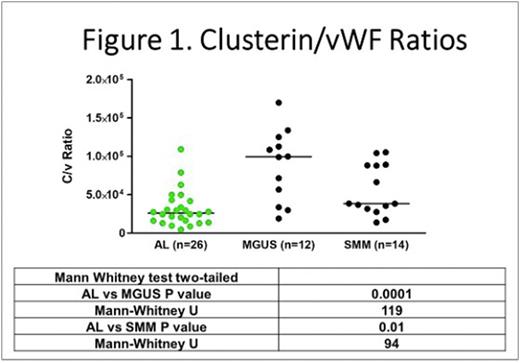
Results: Twelve MGUS and 16 SMM patients, all λ-isotype, enrolled on NCT04615572, met FLC criteria and had marrow shipped to Tufts; 2 of the SMM patients were found to have AL and are included with 24 AL λ-type patients whose marrow aspirates were obtained in the same time period. There were no differences in age or gender, but the percentage of marrow plasma cells in SMM and AL patients were significantly greater than in MGUS patients. Comparisons of AL, SMM and MGUS iFLC λ levels did not achieve statistical significance. Medians were 338, 182 and 346 mg/L respectively. Marrow plasma from AL patients had significantly lower C/v ratios than those in either MGUS or SMM specimens (Figure 1). There was no correlation between λ FLC and the C/v ratio (r = -0.20, P > 0.05). Compared to normal individuals (n=20) with a median C/v ratio of 16.9x104 (range, 2.7-56.5), the C/v ratio in peripheral blood in newly diagnosed AL patients (n=15) was significantly lower at a median of 1.5x104 (0.8-2.0) (P<0.01, Mann-Whitney two-tailed).
Conclusion: These preliminary data suggest that the C/v ratio is a potential parameter of interest in the construction of a likelihood algorithm for AL in patients with monoclonal gammopathies. The rationale for the ratio is that with progression during the prodromal period prior to significant organ damage clusterin may decrease while vWF may increase. Whether peripheral blood may provide a useful source of plasma is unclear and whether ratios below a threshold or changes in the ratio over time may signal risk of AL or be significant remain questions for further exploration.
Disclosures
Wong:Janssen: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Research Funding; Fortis: Research Funding; Caelum: Research Funding; Dren Bioscience: Consultancy; Catalent Biologics: Consultancy; Patient Discovery: Research Funding. Tuchman:Prothena: Honoraria; Shattuck Labs: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria. Hoffman:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Seagen Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal